Georesistivity Signature of Crystalline Rocks in the Romblon Island Group, Philippines
Leo T. Armada1,*, Carla B. Dimalanta1, Graciano P. Yumul, Jr.1,2, and Rodolfo A. Tamayo, Jr.1
1Tectonics and Geodynamics Group, National Institute of Geological Sciences
University of the Philippines, Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines 1101
2Department of Science and Technology, Bicutan, Taguig City, Philippines 1631
*This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
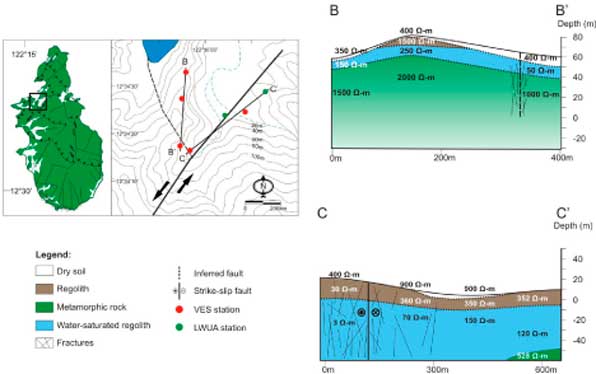
Georesistivity data from the survey site in Bagacay, Romblon Island (Black Square in inset map). Unweathered crystalline rocks in section B-B’ are characterized by high resistivities (1000 to 2000 Ω-m). The fractured and weathered portions near the fault shown in section C-C’ exhibit lower resistivities.
ABSTRACT
Georesistivity surveys were conducted in the tectonically complex Romblon Island Group, Philippines to assess the groundwater potential of the crystalline rocks found in the area. Vertical electrical sounding (VES) using Schlumberger array with a maximum spread (AB/2) of 300 meters was used during the survey; this array provided vertical images of depth up to 60 meters. The VES results show significantly lower resistivity values for the regolith (~10 to 250 ohm-meters) compared with the resistivity values of the parent units (i.e., ultramafic rocks: ~ 800 ohm-meters and metamorphic rocks: 1000 to 2000 ohm-meters). These resistivity values are attributed to the elevated groundwater content of the regolith compared with the unweathered parent rocks. Furthermore, thick regoliths were formed in areas adjacent to pre-existing faults and fracture zones in the area. The flow of groundwater through the fissures in the crystalline rocks possibly contributes to enhancing deeper levels of weathering to produce the low-resistivity regoliths observed. Also, the regoliths, with an average thickness of 35m, serve as zones of enhanced groundwater potential in the Romblon Island Group because of their relative thick overburden and low resistivity......
REFERENCES
ABARQUEZ OE 1969. Resistivity soundings on sand and gravel deposits at Malaya, Pililla, Rizal. J Geol Soc Philipp 23: 113-119.
[ADB] ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK. 1999. Project performance audit report on the second island provinces rural water supply sector project in the Philippines. Mandaluyong City, Philippines: Asian Development Bank. 50p.
ADEPELUMI AA, YI M-J, KIM J-H, AKO BD, SON JS. 2006. Integration of surface geophysical methods for fracture detection in crystalline bedrocks of southwestern Nigeria. Hydrogeol J 14: 1284-1306.
CHANDRA S, RAO VA, KRISHNAMURTHY NS. 2006. Integrated studies for characterization of lineaments used to locate groundwater potential zones in a hard rock region of Karnataka, India. Hydrogeol J 14: 1042-51.
CONNELL S, SCROMEDA N, KATSUBE TJ, MWENIFUMBO J. 2000. Electrical resistivity characteristics of mineralized and unmineralized rocks from Giant and Con mine areas, Yellowknife, Northwest Territories. Geological Survey of Canada, Current Res (2000-E9) Rpt, 9p.
DAS UC , VERMA SK. 1980. Digital linear filtering for computing type curves for the two-electrode system of resistivity sounding. Geophys Prosp 28: 610-619.
DEWANDEL B, LACHASSAGNE P, BOUDIER F, AL-HATTALI S, LADOUCHE B, PINAULT JL, ALSULEIMANI Z. 2005. A conceptual hydrogeological model of ophiolite hard-rock aquifers in Oman based on a multiscale and multidisciplinary approach. Hydrogeol J 13: 708-726.
DUTTA S, KRISHNAMURTHY NS, ARORA T, RAO VA, AHMED S, BALTASSAT JM. 2006. Localization of water bearing fractured zones in a hard rock area using integrated geophysical techniques in Andhra Pradesh, India. Hydrogeol J 14: 760-766.
HSU SK, YEH Y-C, DOO W-B, TSAI C-H. 2004. New bathymetry and magnetic lineations identifications in the northernmost South China Sea and their tectonic implications. Mar Geophys Res 25: 29-44.
ISRAIL M, AL-HADITHI M, SINGHAL DC, KUMAR B. 2006. Groundwater-recharge estimation using a surface electrical resistivity method in the Himalayan foothill region, India. Hydrogeol J 14: 44-50.
KELLETT R, BAUMAN P. 2004. Mapping groundwater in regolith and fractured bedrock using ground geophysics: A case study from Malawi, SE Africa. Can Soc Explor Geophys Recorder 24-33.
KOEFOED O. 1979. Geosounding Principle, Volume 1. Amsterdam: Elsevier 276p.
LENKEY L, HAMORI Z, MIHALFFY P. 2005. Investigating the hydrogeology of a water-supply area using direct-current vertical electrical sounding. Geophys 70: 11-19.
[LWUA] LOCAL WATER UTILITIES ADMINISTRATION. 2004. Report on well site evaluation: Georesistivity survey, Romblon Water District, Romblon. Technical Report, Quezon City: Local Water Utilities Administration. 65p.
LOUIS IF, LOUIS FI, GRAMBAS A. 2002. Exploring for favorable groundwater conditions in hardrock environments by resistivity imaging methods: Synthetic simulation approach and case study example. J Elec Electron Engg Spec Issue 1-14.
MACDONALD AM, DAVIES J. 2000. A brief review of groundwater for rural water supply in sub-Saharan Africa. Notthingham, United Kingdom: British Geological Survey. 13p.
[MGB] MINES AND GEOSCIENCES BUREAU. 1997. Water availability map of the Philippines. Quezon City, Philippines: Mines and Geosciences Bureau.
MCNEILL JD. 1990. Use of electromagnetic methods for groundwater studies. In: Ward SH (ed) Geothechnical and Environmental Geophysics, Volume 1, Review and Tutorial. Soc Explor Geophys Inv No. 5: 107-112.
MONDAL NC, RAO VA, SINGH VS, SARWADE DV. 2008. Delineation of concealed lineaments using electrical resistivity imaging in granitic terrain. Curr Sci 94: 1023-30.
OWEN RJ, GWAVAVA O, GWAZE P. 2005. Multielectrode resistivity survey for groundwater exploration in the Harare greenstone belt, Zimbabwe. Hydrogeol J 14: 244-252.
OWEN R, MAZITI A, DAHLIN T. 2007. The relationship between regional stress field, fracture orientation and depth of weathering and implications for groundwater prospecting in crystalline rocks. Hydrogeol J 15: 1231-38.
RAMOS NT, DIMALANTA CB, BESANA GM, TAMAYO RAJ, YUMUL GPJ, MAGLAMBAYAN VB. 2005. Seismotectonic reactions to the arccontinent convergence in Central Philippines. Res Geol 55: 199-206.
RAO YS, REDDY TVK, NAYUDU PT. 2000. Groundwater targeting in a hard-rock terrain using fracture pattern modeling, Niva Pradesh, India. Hydrogeol J 8: 494-502.
SHARMA SP, BARANWAL VC. 2005. Delineation of groundwater-bearing fracture zones in a hard rock area integrating very low frequency electromagnetic and resistivity data. J App Geophys 57: 155-166.
SRINIVASA GOWD S. 2004. Electrical resistivity surveys to delineate groundwater potential aquifers in Peddavanka watershed, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Env Geol 46: 118-131.
STIRLING EDWARDS L, GONZALES CP. 1984. Resistivity survey of the sand-dunes aquifer, Paoay Lake and Currimao, Ilocos Norte. The Philippine Geologist 38: 50-69.
SUBBA RAO N. 2003. Groundwater prospecting and management in an agro-based rural environment of crystalline terrain of India. Env Geol 43: 419-431.
SULTAN SA, MANSOUR SA, SANTOS FAM. 2008. A hydrogeophysical investigation of the Ain Mousa area, near Cairo, Egypt. Bull Eng Geol Environ 67: 111-117.
SURRETTE M, ALLEN DM, JOURNEAY M. 2007. Regional evaluation of hydraulic properties in variably fractured rock using a hydrostructural domain approach. Hydrogeol J 16: 11-30.
TAYLOR B, HAYES DE. 1980. The tectonic evolution of the South China Basin. In: Hayes DE (ed) The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands. Am Geophys Monogr Series 23: 89-104.
TAYLOR RC, HOWARD KWF. 1998. Post-Paleozoic evolution of weathered land surfaces in Uganda by tectonically controlled deep weathering and stripping. Geomorph 25: 173-192.
TAYLOR RC, HOWARD KWF. 1999. Lithological evidence for the evolution of weathered mantles in Uganda by tectonically controlled cycles of deep weathering and stripping. Catena 35 (1): 65-94.
TAYLOR RC, HOWARD KWF. 2000. A tectonogeomorphic model of the hydrogeology of deeply weathered crystalline rock: Evidence from Uganda. Hydrogeol J 8: 279-294.
TELFORD WM, GELDART LP, SHERIFF RE. 1976. Applied Geophysics. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. 860p.
YADAV GS, SINGH. 2008. Integrated surveys for delineation of fractures for groundwater exploration in hard rock areas. J Applied Geophys 62: 301-312.
YUMUL GPJ, DIMALANTA CB, TAMAYO RAJ, MAURY RC. 2003. Collision, subduction and accretion events in the Philippines: a synthesis. Isl Arc 12: 77-91.
YUMUL GPJ, DIMALANTA CB, MARQUEZ EJ, MAGLAMBAYAN VB. 2008. Tectonic setting of a composite terrane: A review of the Philippine island arc system. Geosci J 12: 7-17.
YUMUL GPJ, DIMALANTA CB, TAMAYO RA JR. 2005. Indenter-tectonics in the Philippines: Example from the Palawan microcontinental block – Philippine mobile belt collision. Res Geol 55: 189-198.
ZOUHRI L, CARLIER E, BEN KABBOUR B, TOTO EA, GORINI C, LOUCHE B. 2008. Groundwater interaction in the coastal environment: hydrochemical, electrical and seismic approaches. Bull Eng Geol and Env 67: 123-128.









