Synthesis of [RMIM] Acetate Halogen-Free Ionic Liquids for Use as Greener Solvents in Diels-Alder Reaction
Susan D. Arco1*, Rosalie T. Laxamana2, Ofelia D. Giron1, and Judy M. Obliosca1
1Institute of Chemistry and 2Natural Sciences Research Institute
University of the Philippines, Diliman, Quezon City 1101
*This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
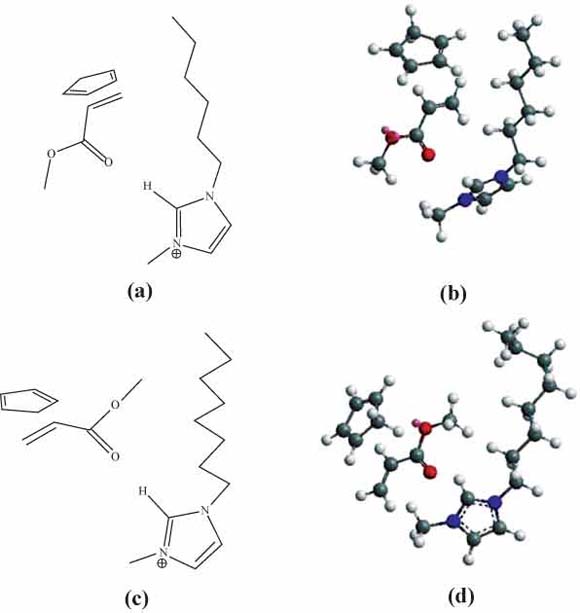
Representations of the endo- and exo- TS in the Diels-Alder reaction of methyl acrylate and cyclopentadiene in [RMIM]OAc medium; (a) and (c) are 2D models of endo TS and exo TS, respectively; (b) and (d) are 3D models of endo TS and exo TS, respectively.
ABSTRACT
A halogen-free ionic liquid 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate, [RMIM]OAc, with its cation based on 1-alkyl-3-methyl imidazolium and with the halogen-free anion acetate (OAc) was synthesized. This ionic liquid’s distinctive solvent properties and its application as greener solvent for the Diels-Alder reaction were examined. Its efficiency as medium for the Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and methyl acrylate was evaluated in terms of product yield and stereoselectivity. Using these parameters, [RMIM]OAc was compared with other solvents such as benzene, methanol, and water as alternative solvent for the Diels-Alder reaction. Results showed a decrease in product yield as the length of the alkyl group chain on the imidazolium cation is increased from C6 to C12. In terms of stereoselectivity, there is a general preference for the endo-product in all of the solvents tested. The endo-selectivity obtained with [HMIM]OAc (endo:exo=91:9) is remarkably high and is more desirable compared to that obtained with water (endo:exo=76:24)......
REFERENCES
ABBOTT AP, CAPPER G, DAVIES DL, RASHEED RK, TAMBYRAJAH V. 2002. Quaternary Ammonium Zinc- or Tin- Containing Ionic Liquids: Water Insensitive, Recyclable Catalysts for Diels Alder Reactions. Green Chemistry 4: 24-26.
AGGARWAL A, LANCASTER NL, SETHI AR, WELTON T. 2002, The role of hydrogen bonding in controlling the selectivity of Diels–Alder reactions in room-temperature ionic liquids. Green Chemistry 4: 517-520.
BERSON JA, HAMLET Z, MUELLER, WA. 1962. The Correlation of Solvent Effects on the Diels Alder Reactions by Means of Linear Free Energy Relationships. A New Empirical Measure of Solvent Polarity. J Am Chem Soc 84: 297-304.
CLARKE D, ALI M, CLIFFORD A, PARRATT A, ROSE P, SCHWINN D, BANNWARTH W, RAYNER C. 2004. Reactions in Unusual Media. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 4: 729-771.
EARL MJ, MCCORMAC PB, SEDDON KR 1998. DielsAlder Reaction in Ionic Liquids. Chem Commun 71: 2245-46.
FISHER T, SETHI T, WELSON T, WOOLF J. 1999. Diels-Alder Reaction in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. Tetrahedron Lett 40: 793-796.
GARRETT RH, GRISHAM CM. 2005. Biochemistry. Singapore: Brooks/Cole, Thomson Learning Asia. 1085p.
HOFFMANN R, WOODWARD RB. 1965. Orbital Symmetries and Endo-Exo Relationships in Concerted Cycloaddition Reactions. J Am Chem Soc 87: 4388-89.
HOLBREY JD, SEDDON KR. 1999. Ionic Liquids. Clean Products and Processes 1: 223-236.
JAEGER DA, TUCKER CE. 1989. Diels-Alder Reactions in Ethylammonium Nitrate, A Low-Melting Fused Salt. Tetrahedron Lett 30: 1785-88.
KOEL M. 2000. Physical and Chemical Properties of Ionic Liquids Based on the Dialkylimidazolium Cations. Proc Estonian Acad Sci Chem 49(3): 145-155.
OLIVIER-BOURBIGOU H, MAGNA L. 2002. Ionic Liquid Perspectives for Organic and Catalytic Reactions. J Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical 3484: 1-19.
SEDDON KR.1998. Ionic Liquids for Clear Technology. In: Molten Salt Forum. Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Molten Salt Chemistry and Technology, Vol. 5-6. Wendt H. (ed); 1988 August; Dresden, Germany: Trans Tech Publications, Inc. p. 53-62.
WELTON T. 1999. Room Temperature Ionic Liquids: Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. Chemical Reviews 99: 2071-83.









